What is an SSD?
What is a Solid- State Drive?
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a new age of storage devices used in computers. SSDs take over traditional mechanical hard disks by using flash-based memory, which is no doubt faster. Earlier hard-disk storage technologies run slower, which often makes your computer run slower than it should, it bottlenecks the capabilities of the system. SSDs speed up computers significantly due to their low read-access times and fast throughputs. Here’s all you need to know.

It is a storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data as 1s and 0s, typically using flash memory, but functioning as secondary storage. It is also sometimes called a solid-state disk, even though SSDs have the absence of physical spinning disks and read-write heads used in hard disk drives and floppy disks. That is the reason they got their names as Solid-State because they do not have any moving parts.
As these drives have the absence of disks and have no moving parts, they only have integrated circuits where the data are stored on. This also provides them with an advantage of the size it can move down to a size of a mini sticky note or the size of a chewing gum packet. For example M.2 form factor SSD or even to a size of postage stamps which can be mounted directly to any device. Their capacity to size ratio makes them compatible with smaller and compact devices.
The downside of SSD right now is that these are more expensive than the HDDs in the per amount of storage (in GB/TB). But the gap is reducing as the prices of SSD are reducing.
Different Types of SSDs

To classify Solid State Drives – SSDs into groups we here classified them according to the interface they use:
- PCIe and NVMe SSDs: These drives use the high-speed bandwidth and low latency PCI Express interface to provide blazing fast communication between the SSD, CPU and RAM. Some SSDs uses the Nonvolatile Memory Express Standard (NVMe) which offers higher input-output per second (IOPS) and even lower latency than SATA.
- SATA (mSATA III, SATAIII), and traditional SSDs: These SSDs uses serial advanced technology attachment (SATA) an older interface that was designed specifically for storage application with speed up to 6 Gbit/s or about 600MB per second. SATA is slowly being eliminated by NVMe, which is significantly faster. But older PCs having SATA interface in them can upgrade to SATA SSDs can see a significant rise in performance.
SSDs are available in a variety of storage capacities, starting from 32 GB and up to 5 TB in the consumer space. In the Enterprise segment, the SSD with higher capacity are also available. The common size today is 250GB, 500GB and 1TB, which is plenty of capacity for an OS and programs and other personal files. These sizes are perfect for a decent PC build.
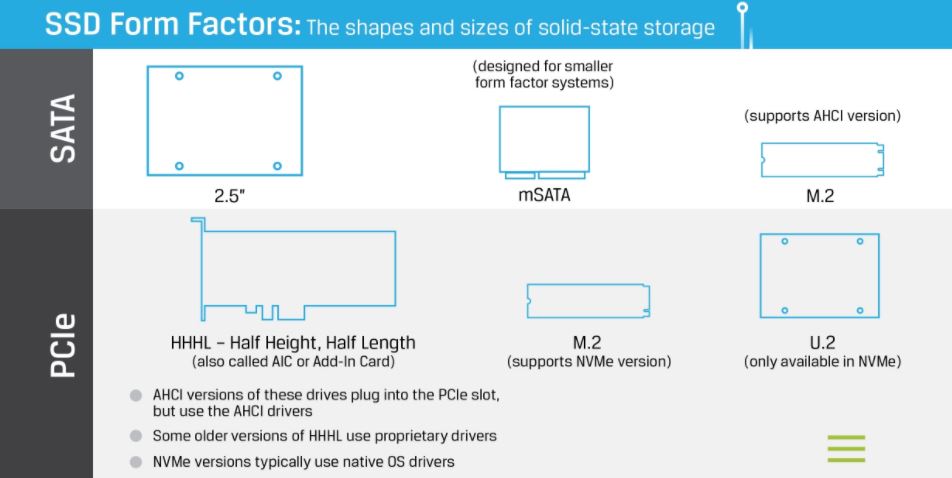
Here in this infographic from a community article of Kingston shows different form factors of SSDs.
The ExaDrive EDDCT100/EDDCS100 from Nimbus Data is Biggest Drive or Solid-state drive to this date.
Use of SSDs
SSDs have specific benefits in the following areas:
Business: Companies functioning on huge amounts of data like programming environments, videography or data analysis generally rely on SSDs, as access times and file-transfer speeds are demanding.
Gaming: The gaming segment or specifically Gaming PCs have always pushed the limits of modern computing technology, using the most expensive equipment for getting superior gaming performance and experience. That is notably true for storage, as modern games continuously load and write files.
Mobility: SSDs have low power demands, thus adding to better battery life in movable devices like laptops and tablets. SSDs are also shock resistant. SSDs can withstand 1500G’s, 25times more than HDDs, which cuts the chances of data loss when mobile devices are dropped or in a highly flexible demanding environment.
Servers: Enterprise segments or servers need SSDs to get fast reads and writes speeds in order to properly serve their client PCs. Using SSDs in servers reduces the power consumption, SSDs in the enterprise segment moves up to 100TB in capacity for each drive, providing them with a factor of advantage i.e ratio of capacity to size.
